Talking About Eroom’s Law
Where I Learn to Version My Projects
Introduction
Computer nerds know about Moore’s Law. Coined by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore in 1965, Moore’s Law states that the number of transistors in an integrated circuit will double roughly every two years with little increase in costs. For consumers, that means we will have access to better computers at reasonable (hopefully) prices (Investopedia for Moore info (see what I did?)). Moore’s law has been an important idea underpinning technology, business, and the world at large.
Why mention Moore’s Law at all?
Well, for the drug development space, there is a term, coined by Dr. Jack Scannell in 2012 (Nature Reviews Drug Discovery), that states drug discovery has become slower and more expensive over time. He and his co-authors coined this phenomenon Eroom’s Law (Moore’s Law spelled backwards) to describe this trend. Many researchers in the field has had a sense of this. The R&D of drugs can be astronomical. It is estimated that the costs for a U.S. FDA approved drug takes roughly 10 years and upward of $2 Billion USD or more (wiki here). And these metrics are obviously ‘best case’ scenarios.
Does Eroom’s Law Hold True Today?
Recently, there has been discussion of Eroom’s Law on my social media feed. A quick google search will show several interesting articles on the topic. There is one by Scientific American in 2019 wondering if human organs on chip could combat increasing R&D costs (here). A few years ago I read an analysis on ‘breaking’ Eroom’s Law, published in Nature Reviews Discovery (here).
This is especially of note as AI has become all the rage over recent years. AI has been touted as a method of reducing the time and cost of drug development. Popular AI focused companies, such as Insilico and Exscientia, were one of the first in the drug discovery space and now have many drug candidates in the pipeline. Plus, other technologies have become cheaper. Genome sequencing has rapidly decreased from $100 Million USD to below $1,000 USD today (or possibly below $100 USD according to this article here). Will Eroom’s Law hold true in the future?
Trend’s Today
To look at this, I scraped together information from public resources to piece together my own Eroom’s Law graph. The information came from the US FDA CDER New Molecular Entities (here) and from the 2025 PhRMA Annual Membership Survey (here). The former was used to obtain the number of novel drugs approved from 1987 to 2024, while the latter was used to obtain estimates of the amount spent on R&D. The information was collected and processed in python (a future post).
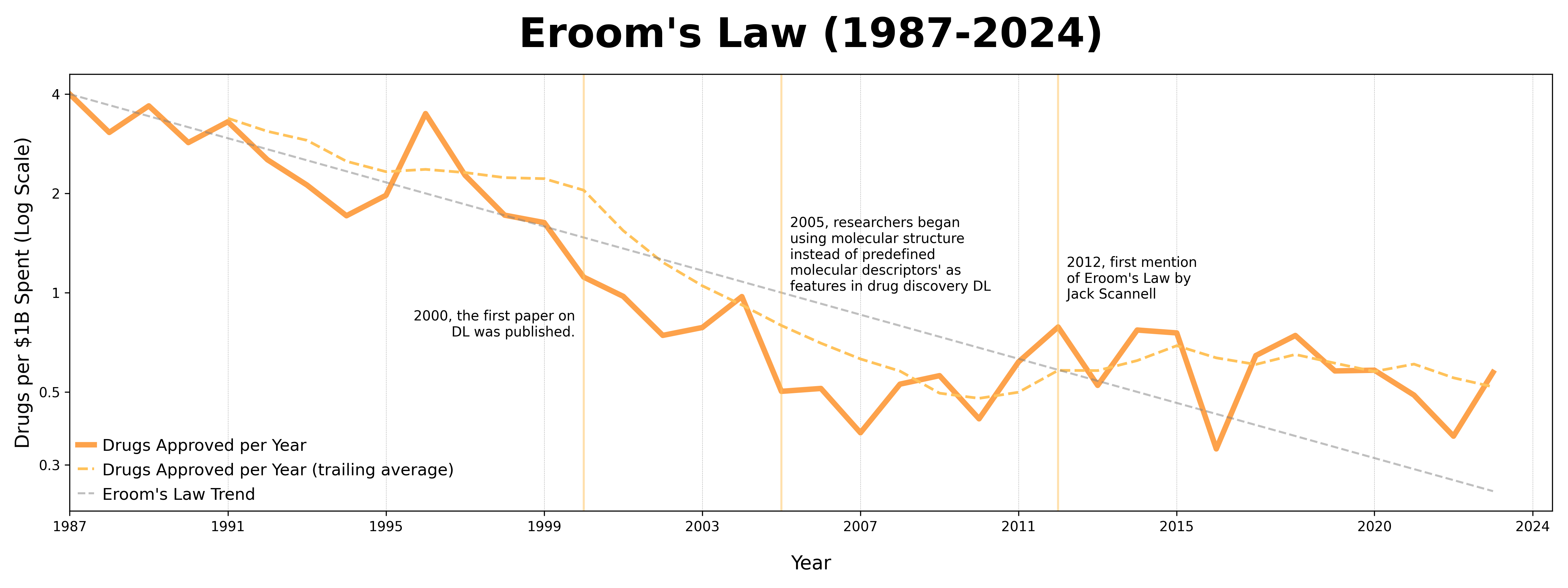
The figure is striking to me in many ways. In the period between 2012 - 2015, it seems that Eroom’s Law was holding, with a rough return of 0.4 approved drug per $1 Billion USD spent. However, this is a short timeframe. More drugs have been approved since. True, they are still expensive compared to the late 80’s and 90’s, but we see a small curve upwards beginning in the late 2010s.
Now there is a crucial technology permeating through our lives - AI. Would AI break Eroom’s Law in the near future? Personally, I have two conflicting viewpoints on this.
Will AI Increase ‘Drug Slop’?
In my opinion, AI will not solve everything. We see that now in the current economy, with AI tools being pedaled by companies and ‘AI slop’ constantly invading our screens. This phenomenon is also happening in the scientific sphere. Already we have seen bad actors use AI to clog up scientific journals (a discussion here).
In drug discovery, AI can vastly reduce the time it takes to identify drug candidates. But does is it truly the best candidate or is it ‘AI drug slop’? Identifying and selecting a compound is made easier with AI, but if the practitioner does not understand the basics, does the AI program truly help?
A crucial bottleneck in drug discovery remains - actually testing the drug. AI cannot do that. And many models are imperfect. With the increase in ‘AI drug slop’, researchers may be spending more time trying to prase out which drug to test. This can have financial implications, with many of the ‘AI drug slop’ taking up a share of the testing budget.
Will AI Help Us Focus on Better Candidates?
On the flip side, AI can help us focus on better drug candidates. A few years ago, it was unreasonable to scan through Billions of molecules. AI allows researchers to do that. Combine this technology with researchers experience with previous drug development campaigns and someone with good business decision making skills, and I can truly see AI revolutionizing drug development.
It isn’t easy. It would require a retooling of our current drug development pipeline. But like many things, perhaps it is time for an overhaul. Since the late 2010s, the Eroom’s Law trend seems to be holding steady. I can see, if AI is integrated properly, the trend to finally bend upwards.
Conclusion
It will be interesting to see what this figure looks like in another 10 years. By then we should have a more mature AI developers in drug discovery. To me, that means better computers, better algorithms, better operating procedures to compare models. It is an exciting time to be in the drug discovery space.